1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
|
#include "opencv2/opencv.hpp"
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <random>
std::tuple<int, int> GetSample(const int& index_size,
const std::vector<std::tuple<int, int>>& sampled_indexes)
{
assert(index_size > 2);
static std::random_device rd;
static std::mt19937_64 gen(rd());
static std::uniform_int_distribution<int> dist(0, index_size - 1);
while (true)
{
int index1 = dist(gen);
int index2 = dist(gen);
if (index1 == index2) { continue; }
int min_index = std::min(index1, index2);
int max_index = std::max(index1, index2);
bool has_sampled = false;
for (auto& [i, j] : sampled_indexes)
{
if (min_index == i && j == max_index)
{
has_sampled = true;
break;
}
}
if (has_sampled) { continue; }
else { return { min_index, max_index }; }
}
}
void Show(const std::vector<cv::Point2f>& all_pts,
const std::vector<cv::Point2f>& inlier_pts,
const std::vector<cv::Point2f>& sample_pts,
const int windows_size,
const double a,
const double b,
const double c)
{
cv::Mat image = cv::Mat(windows_size, windows_size, CV_8UC3, cv::Scalar::all(255));
for (auto& p : all_pts)
{
if (p.x >= 0 && p.x < windows_size && p.y >= 0 && p.y < windows_size)
{
cv::circle(image, p, 5, { 0, 0, 255 }, -1);
}
}
cv::Point2f p1, p2;
if (a * b > 0)
{
p1.x = windows_size - 1;
p1.y = -(a * p1.x + c) / b;
p2.x = 0;
p2.y = -(a * p2.x + c) / b;
}else
{
p1.y = 0;
p1.x = -(b * p1.y + c) / a;
p2.y = windows_size - 1;
p2.x = -(b * p2.y + c) / a;
}
cv::line(image, p1, p2, { 0, 0, 0 }, 2, cv::LINE_AA);
for (auto& p : inlier_pts)
{
if (p.x >= 0 && p.x < windows_size && p.y >= 0 && p.y < windows_size)
{
cv::circle(image, p, 5, { 255, 0, 0 },-1);
}
}
for (auto& p : sample_pts)
{
if (p.x >= 0 && p.x < windows_size && p.y >= 0 && p.y < windows_size)
{
cv::circle(image, p, 5, { 0, 255, 0 }, -1);
}
}
cv::imshow("ransac-line-fit", image);
cv::waitKey(500);
}
std::tuple<double, double, double> LineFit(const std::vector<cv::Point2f>& pts)
{
cv::Vec4f line;
cv::fitLine(pts, line, cv::DIST_L2, 0, 1e-2, 1e-2);
double a = line[1];
double b = -line[0];
double c = line[0] * line[3] - line[1] * line[2];
return { a, b, c };
}
void RansacLinefit(const std::vector<cv::Point2f>& pts,
const float inlier_threshold,
std::vector<int>& inlier_indexes)
{
if (pts.size() <= 3) { return; }
if (inlier_threshold < 1e-6) { return; }
//1. 参数检查,初始化
int iterate_nums = 500; //迭代次数
float sample_points_min_distance = 5.0f; //两个采样点之间最小的距离
std::vector<std::tuple<int, int>> sampled_indexes;//已经采样的坐标点
sampled_indexes.reserve(iterate_nums);
std::vector<int> is_inlier(pts.size(), 0);
std::vector<int> is_inlier_tmp(pts.size(), 0);
int max_inlier_num = 0;
int sample_count = 0;
//2. 循环迭代
while (sample_count < iterate_nums)
{
//3. 随机抽取两点(采样)
auto [p1, p2] = GetSample(pts.size(), sampled_indexes);
if (std::abs(pts[p1].x - pts[p2].x) < sample_points_min_distance
&& std::abs(pts[p1].y - pts[p2].y) < sample_points_min_distance)
{
continue;
}
else
{
sampled_indexes.push_back({ p1, p2 });
}
//4. 直线拟合
auto [a, b, c] = LineFit({ pts[p1], pts[p2] });
//5. 基于拟合的直线区分内外点
int inlier_num = 0;
std::vector<cv::Point2f> inliers;
for (int i = 0; i < pts.size(); i++)
{
auto& p = pts[i];
is_inlier_tmp[i] = 0;
if (std::abs(a * p.x + b * p.y + c) < inlier_threshold)
{
is_inlier_tmp[i] = 1;
inlier_num++;
inliers.push_back(pts[i]);
}
}
Show(pts, inliers, { { pts[p1], pts[p2] } }, 500, a, b, c);
if (inlier_num > max_inlier_num)
{
max_inlier_num = inlier_num;
is_inlier = is_inlier_tmp;
}
//6. 更新迭代的最佳次数
if (inlier_num == 0)
{
iterate_nums = 500;
}
else
{
double epsilon = 1.0 - double(inlier_num) / (double)pts.size(); //野值点比例
double p = 0.99; //所有样本中存在1个好样本的概率
double s = 2.0;
iterate_nums = int(std::log(1.0 - p) / std::log(1.0 - std::pow((1.0 - epsilon), s)));
}
sample_count++;
}
//7. 基于最优的结果所对应的内点做最终拟合
std::vector<cv::Point2f> inliers;
inliers.reserve(max_inlier_num);
for (int i = 0; i < is_inlier.size(); i++)
{
if (1 == is_inlier[i])
{
inliers.push_back(pts[i]);
}
}
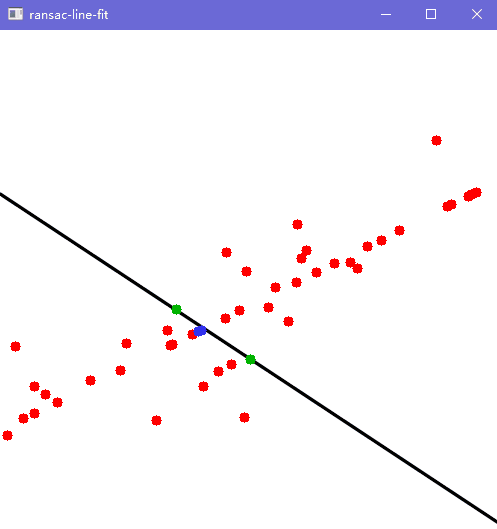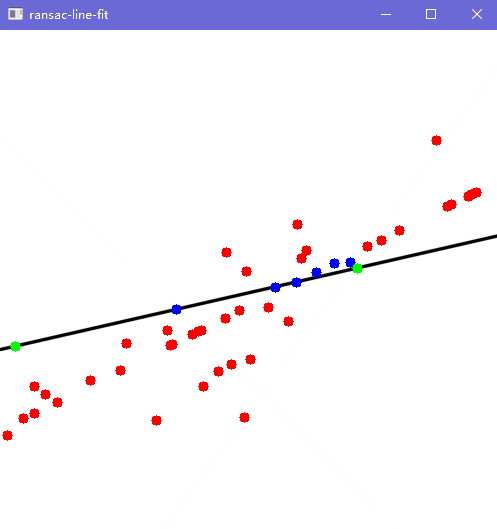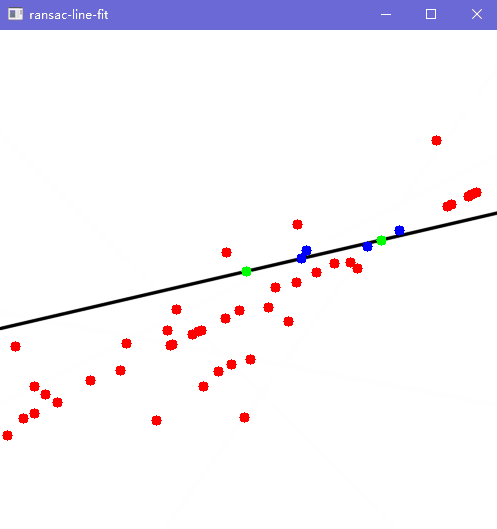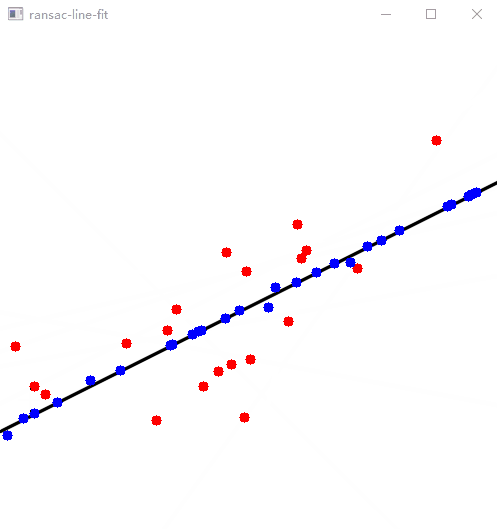
auto [a, b, c] = LineFit(inliers);
std::cout << " a = " << a << " b = " << b << " c = " << c << std::endl;
Show(pts, inliers, {}, 500, a, b, c);
cv::waitKey(0);
}
int main()
{
double a = 1.0, b = 2.0, c = -800.0;
std::random_device rd;
std::mt19937_64 gen(rd());
std::uniform_int_distribution<int> dist(0, 499);
std::normal_distribution<double> disty(0, 50);
std::normal_distribution<double> distx(0, 10);
std::vector<cv::Point2f> pts;
for (int i = 1; i < 50; i ++)
{
float x = dist(gen);
float y = -(a * x + c) / b;
if (i % 2 != 0)
{
x += distx(gen);
y += disty(gen);
}
pts.emplace_back(x, y);
}
std::vector<int> inliers_indexes;
RansacLinefit(pts, 10, inliers_indexes);
return 0;
}
|